Raees wants to build a new tank to hide his illegal liquor . He comes up with some designs . Now he asks you to find out maximum units of liquor he can fill in the tank.
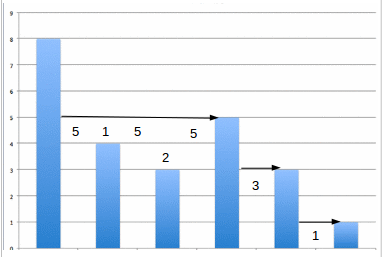
You are given N elements , corresponding to heights of walls . See the figure for input 0 ,8 ,0 ,4 ,0 ,3 ,0 ,5 ,0 ,3 ,0 ,1 ,0.
Maximum amount of liquor that can be filled is 5 + 1 + 5 + 2 + 5 + 3 + 1 = 22.
Eg : For input 4 ,2 ,4 ,3 Output will be 2 .
INPUT
- First line of input contains a single integer N.
- Second line of input contains N non-negative integers ( A0 --- A(n-1) ).
OUTPUT
- Single integer , answer to the Raees's question.
CONSTRAINTS
- 1 <= N <= 1000
- 1 <= Ai <= 1000
SAMPLE INPUT
13
0 8 0 4 0 3 0 5 0 3 0 1 0
SAMPLE OUTPUT
22
Code:
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
import java.math.*;
import java.lang.*;
import static java.lang.Math.*;
public class Q1
{
static class InputReader
{
private InputStream stream;
private byte[] buf = new byte[1024];
private int curChar;
private int numChars;
private SpaceCharFilter filter;
public InputReader(InputStream stream)
{
this.stream = stream;
}
public int read()
{
if (numChars==-1)
throw new InputMismatchException();
if (curChar >= numChars)
{
curChar = 0;
try
{
numChars = stream.read(buf);
}
catch (IOException e)
{
throw new InputMismatchException();
}
if(numChars <= 0)
return -1;
}
return buf[curChar++];
}
public String nextLine()
{
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String str = "";
try
{
str = br.readLine();
}
catch (IOException e)
{
e.printStackTrace();
}
return str;
}
public int nextInt()
{
int c = read();
while(isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-')
{
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
int res = 0;
do
{
if(c<'0'||c>'9')
throw new InputMismatchException();
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
}
while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public long nextLong()
{
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-')
{
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
long res = 0;
do
{
if (c < '0' || c > '9')
throw new InputMismatchException();
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
}
while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res * sgn;
}
public double nextDouble()
{
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
int sgn = 1;
if (c == '-')
{
sgn = -1;
c = read();
}
double res = 0;
while (!isSpaceChar(c) && c != '.')
{
if (c == 'e' || c == 'E')
return res * Math.pow(10, nextInt());
if (c < '0' || c > '9')
throw new InputMismatchException();
res *= 10;
res += c - '0';
c = read();
}
if (c == '.')
{
c = read();
double m = 1;
while (!isSpaceChar(c))
{
if (c == 'e' || c == 'E')
return res * Math.pow(10, nextInt());
if (c < '0' || c > '9')
throw new InputMismatchException();
m /= 10;
res += (c - '0') * m;
c = read();
}
}
return res * sgn;
}
public String readString()
{
int c = read();
while (isSpaceChar(c))
c = read();
StringBuilder res = new StringBuilder();
do
{
res.appendCodePoint(c);
c = read();
}
while (!isSpaceChar(c));
return res.toString();
}
public boolean isSpaceChar(int c)
{
if (filter != null)
return filter.isSpaceChar(c);
return c == ' ' || c == '\n' || c == '\r' || c == '\t' || c == -1;
}
public String next()
{
return readString();
}
public interface SpaceCharFilter
{
public boolean isSpaceChar(int ch);
}
}
public static int[] SOE()
{
int n=(int)(1e5); //till which digit
int ip[]=new int[n];
for(int i=2;i<(int)Math.sqrt(n);i++)
{
if(ip[i]==0)
{
for(int j=i*i;j<n;j=j+i)
{
ip[j]++;
}
}
}
ip[1]++; //counts 1 and 0 as primes
ip[0]++;
return ip;
}
private static long gcd(long a, long b)
{
while (b > 0)
{
long temp = b;
b = a % b; // % is remainder
a = temp;
}
return a;
}
private static long gcd(long[] input)
{
long result = input[0];
for(int i = 1; i < input.length; i++)
result = gcd(result, input[i]);
return result;
}
private static long lcm(long a, long b)
{
return a * (b / gcd(a, b));
}
private static long lcm(long[] input)
{
long result = input[0];
for(int i = 1; i < input.length; i++)
result = lcm(result, input[i]);
return result;
}
public static void Array_2dsort(Integer[][] a)
{
Arrays.sort(a, new Comparator<Integer[]>() {
public int compare(Integer[] int1, Integer[] int2) {
Integer numOfKeys1 = int1[1]; //about which column u want to sort
Integer numOfKeys2 = int2[1];
return numOfKeys1.compareTo(numOfKeys2);
}
});
}
public static boolean Square(int x)
{
boolean ans=false;
int a=(int)Math.sqrt(x);
if(a*a==x)
ans=true;
return ans;
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception
{
InputReader in=new InputReader(System.in);
PrintWriter w=new PrintWriter(System.out);
int n=in.nextInt();
int a[]=new int[n];
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
a[i]=in.nextInt();
int total=0;
int l[]=new int[n];
int r[]=new int[n];
l[0]=a[0];
r[n-1]=a[n-1];
for(int i=1;i<n;i++)
l[i]=(int)Math.max(l[i-1],a[i]);
for(int i=n-2;i>=0;i--)
r[i]=(int)Math.max(r[i+1],a[i]);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
total+=(int)Math.min(l[i],r[i])-a[i];
w.println(total);
w.close();
}
}
Comments
Post a Comment